文章目录
动画部分在每个平台可以说都是一个常用的部分。如果想让自己的应用或产品的用户体验变得更好,那么动画效果是一个很重要的部分。
Flutter 也提供了大部分的动画效果支持,如常用的渐变动画、位移动画、旋转动画等;特有的一个动画叫 Hero 动画,用来做页面跳转切换到动画效果的。
那么这节课我们将介绍 Flutter 中动画的基本使用详解。Flutter 的基础动画和 Hero 动画都会给大家讲解,并配合一些案例。
1.Flutter动画简单介绍
要学习一个平台的动画使用和原理,那么就要先了解这个平台的动画使用的基本构成。
Flutter 动画的使用一般由这几个部分组成:Animation、AnimationController、CurvedAnimation、Tween 等。
1.1 Animation
它是一个泛型(T),是一个抽象类,可以写成 Animation<int>、Animation<double>、Animation<Offset>、Animation<Color>、Animation<Size> 等等形式。它用于生成指导动画,Animation 提供了这个动画的 value 变化值、操作方法、状态、监听等操作。
1.2 AnimationController
AnimationController 顾名思义是动画生成的控制类,是一个特殊的 Animation 对象,继承自Animation<double>。在屏幕每刷新一帧,就会生成一个新的值,数字的产生与屏幕刷新有关,每秒钟通常会产生 60 个数字。默认值范围是从 0.0 到 1.0。
由于 AnimationController 继承自 Animation<double>,所以它也具有前面讲的 Animation 的方法作用。
我们看下 AnimationController 的一个简单用法:
// 动画控制类,指定了产生数值的上下范围,这里是在3秒钟时间内产生0-2之间小数
final AnimationController _controller = AnimationController(
lowerBound: 0,
upperBound: 2,
duration: const Duration(seconds: 3),
vsync: this);
// 不指定范围,默认产生从0.0到1.0数字,duration时间设置为3秒
final AnimationController _valueController =
AnimationController(duration: const Duration(seconds: 3), vsync: this);
我们看到了 vsync: this 这个属性,通常我们在定义类时需要这样写:
class AnimationSamplesState extends State<AnimationSamples>
with TickerProviderStateMixin {
// 或者 with SingleTickerProviderStateMixin
我们在创建 AnimationController 时,要传入 vsync 参数。vsync 参数作用就是防止执行不必要的动画,消耗不必要的资源,例如锁屏时候屏幕无需刷新和执行动画。
AnimationController 也有很多重要的方法:
// 动画开始方法,可以传起始值,也可以不传
_controller.forward({ double from })
// 动画停止方法
_controller.stop({ bool canceled = true })
// 动画反向播放
_controller.reverse({ double from })
// 动画重置
_controller.reset()
// 动画重复播放设置
_controller.repeat({ double min, double max, bool reverse = false, Duration period })
// 动画销毁
_controller..dispose()
1.3 CurvedAnimation
CurvedAnimation 也是继承自 Animation<double>,主要作用就是将 AnimationController 产生的数值进行不同的曲线变化,也就是将这个动画的运动过程转为一个非线性曲线过程。例如,我们这个数值产生不是线性增加的,而是先快后慢或者慢慢加速再减速,这样就可以产生类似于插值器效果,例如加速再减速动画效果、反弹效果、波浪形运动效果等等。
我们看下大致用法:
// 需要配合AnimationController使用
final Animation<double> animation = CurvedAnimation(
parent: controller,
// 数值产生曲线效果
curve: Curves.easeIn,
// 反向数值产生曲线效果(动画倒放)
reverseCurve: Curves.easeOut,
);
数值产生的曲线效果图如下:
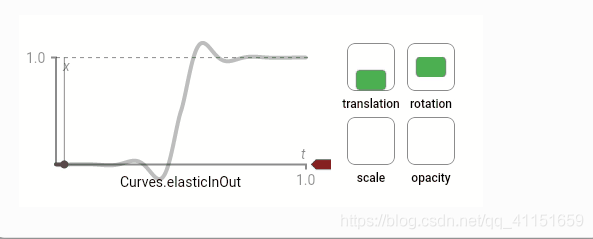
还有很多曲线效果:
class Curves {
static const Curve linear = _Linear._();
static const Curve decelerate = _DecelerateCurve._();
static const Cubic fastLinearToSlowEaseIn = Cubic(0.18, 1.0, 0.04, 1.0);
static const Cubic ease = Cubic(0.25, 0.1, 0.25, 1.0);
static const Cubic easeIn = Cubic(0.42, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0);
static const Cubic easeInToLinear = Cubic(0.67, 0.03, 0.65, 0.09);
static const Cubic easeInSine = Cubic(0.47, 0.0, 0.745, 0.715);
static const Cubic easeInQuad = Cubic(0.55, 0.085, 0.68, 0.53);
static const Cubic easeInCubic = Cubic(0.55, 0.055, 0.675, 0.19);
static const Cubic easeInQuart = Cubic(0.895, 0.03, 0.685, 0.22);
static const Cubic easeInQuint = Cubic(0.755, 0.05, 0.855, 0.06);
static const Cubic easeInExpo = Cubic(0.95, 0.05, 0.795, 0.035);
static const Cubic easeInCirc = Cubic(0.6, 0.04, 0.98, 0.335);
static const Cubic easeInBack = Cubic(0.6, -0.28, 0.735, 0.045);
static const Cubic easeOut = Cubic(0.0, 0.0, 0.58, 1.0);
static const Cubic linearToEaseOut = Cubic(0.35, 0.91, 0.33, 0.97);
static const Cubic easeOutSine = Cubic(0.39, 0.575, 0.565, 1.0);
static const Cubic easeOutQuad = Cubic(0.25, 0.46, 0.45, 0.94);
static const Cubic easeOutCubic = Cubic(0.215, 0.61, 0.355, 1.0);
static const Cubic easeOutQuart = Cubic(0.165, 0.84, 0.44, 1.0);
static const Cubic easeOutQuint = Cubic(0.23, 1.0, 0.32, 1.0);
static const Cubic easeOutExpo = Cubic(0.19, 1.0, 0.22, 1.0);
static const Cubic easeOutCirc = Cubic(0.075, 0.82, 0.165, 1.0);
static const Cubic easeOutBack = Cubic(0.175, 0.885, 0.32, 1.275);
static const Cubic easeInOut = Cubic(0.42, 0.0, 0.58, 1.0);
static const Cubic easeInOutSine = Cubic(0.445, 0.05, 0.55, 0.95);
static const Cubic easeInOutQuad = Cubic(0.455, 0.03, 0.515, 0.955);
static const Cubic easeInOutCubic = Cubic(0.645, 0.045, 0.355, 1.0);
static const Cubic easeInOutQuart = Cubic(0.77, 0.0, 0.175, 1.0);
static const Cubic easeInOutQuint = Cubic(0.86, 0.0, 0.07, 1.0);
static const Cubic easeInOutExpo = Cubic(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
static const Cubic easeInOutCirc = Cubic(0.785, 0.135, 0.15, 0.86);
static const Cubic easeInOutBack = Cubic(0.68, -0.55, 0.265, 1.55);
static const Cubic fastOutSlowIn = Cubic(0.4, 0.0, 0.2, 1.0);
static const Cubic slowMiddle = Cubic(0.15, 0.85, 0.85, 0.15);
static const Curve bounceIn = _BounceInCurve._();
static const Curve bounceOut = _BounceOutCurve._();
static const Curve bounceInOut = _BounceInOutCurve._();
static const ElasticInCurve elasticIn = ElasticInCurve();
static const ElasticOutCurve elasticOut = ElasticOutCurve();
static const ElasticInOutCurve elasticInOut = ElasticInOutCurve();
}
当然我们也可以自己自定义曲线产生的效果:
class ShakeCurve extends Curve {
@override
double transform(double t) {
return math.sin(t * math.PI * 3);
}
}
1.4 Tween
我们知道,默认情况下 AnimationController 产生的数值的范围从 0.0 到 1.0。那么当我们想产生其他范围的数值或类型数据时候怎么办呢?那么 Tween 就是解决这个问题的。
例如,我们可以生成 -100 到 100 的数值、生成颜色值从白色到蓝色的值等等。Tween 也有很多封装子类如:IntTween、ColorTween、AlignmentGeometryTween、DecorationTween、TextStyleTween、RelativeRectTween、RectTween 等。
我们看下简单用法:
final Tween doubleTween = Tween<double>(begin: -100.0, end: 100.0);
final Tween intTween = IntTween(begin: 0, end: 255);
final Tween colorTween = ColorTween(begin: Colors.orange, end: Colors.teal);
// 当然,还可以配合曲线效果CurvedAnimation
Animation<double> _doubleAnimation = Tween<double>(begin: -100.0, end: 100.0).animate(
CurvedAnimation(
parent: _valueController,
// 产生数据的速率曲线效果
curve: Curves.easeIn,
),
)..addListener(() {
setState(() {
// 动画值更新UI
});
});
})..addStatusListener((AnimationStatus status){
// dismissed, forward, reverse, completed
});
当然如果很多动画效果都要我们重复编写这些的话可能很麻烦,所以 Flutter 也封装好了一些常用的动画效果组件,这些效果都是继承自 AnimatedWidget,而 AnimatedWidget 也是继承自StatefulWidget,是一个有状态组件。
例如:AnimatedBuilder、AnimatedModalBarrier、DecoratedBoxTransition、FadeTransition、PositionedTransition、RelativePositionedTransition、RotationTransition、ScaleTransition、SizeTransition、SlideTransition 等,这些组件都是继承自 AnimatedWidget 来进行封装的。
当然按照这个原理,我们也可以自己封装一个某个效果的 AnimatedWidget。例如,我们可以自己封装一个缩放动画的 Widget:
// AnimatedWidget自动帮我们处理addListener()和setState()刷新的事情了,所以我们就可以免去这一步骤了
class ScaleAnimatedWidget extends AnimatedWidget {
final AnimationController animationController;
ScaleAnimatedWidget(
{Key key,
Animation<double> animation,
@required this.animationController})
: super(key: key, listenable: animation);
@override
createState() {
animationController.forward();
return super.createState();
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final Animation<double> animation = listenable;
return Center(
child: Container(
decoration: BoxDecoration(color: Colors.redAccent),
margin: EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 10.0),
height: animation.value * 100,
width: animation.value * 100,
),
);
}
}
我们还可以用 AnimatedBuilder 进行进一步封装。在 Flutter 中使用 AnimatedBuilder 封装的组件有:BottomSheet、ExpansionTile、 PopupMenu、ProgressIndicator、RefreshIndicator、Scaffold、SnackBar、TabBar、TextField 等。
之前用 AnimatedWidget 我们发现,我们只是传入了 Animation 和 AnimationController,然后构建了一个组件,但是在有些时候还是不够灵活和具有通用性。如果我们把一个 Widget 传进来,然后给它设置动画,这样不就更具有通用性和灵活性了吗?例如这个动画 Widget 支持 Image、Text 等等组件。
那么我们看下 AnimatedBuilder 简单用法吧:
class GrowTranstion extends StatelessWidget {
final Widget child;
final Animation<double> animation;
GrowTranstion(this.animation, this.child);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Center(
child: AnimatedBuilder(
animation: animation,
builder: (BuildContext context, Widget child) {
return Container(
child: child,
);
},
child: child,
),
);
}
}
// 在使用的时候直接传入child和动画即可,具有通用性
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return GrowTransition(child: LogoWidget(), animation: animation);
}
...
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return GrowTransition(child: ImageWidget(), animation: animation);
}
那么关于 Flutter 动画的详解部分就大致讲解这么多,基本上所有用法都讲解到了,希望大家可以有所收获。
2.基础动画效果的实现
通过前面讲解这么多,相信大家已经知道了 Flutter 动画使用原理和使用方法步骤了。那么这部分内容就带领大家进行一些效果的实现。
首先我们看一个自定义动画过程的效果实现:
// 定义AnimationController
AnimationController _valueController =
AnimationController(duration: const Duration(seconds: 3), vsync: this);
// 定义Animation
Animation<double> _doubleAnimation = Tween<double>(begin: 0.0, end: 100.0).animate(
CurvedAnimation(
parent: _valueController,
// 产生数据的速率曲线
curve: Curves.easeIn,
),
);
// 可以设置监听,动画状态监听器
_doubleAnimation.addStatusListener((AnimationStatus status) {
if (status == AnimationStatus.forward) {
print('Animation Start');
} else if (status == AnimationStatus.completed) {
print('Animation Completed');
// _controller.reverse();
} else if (status == AnimationStatus.reverse) {
print('Animation Reverse');
} else if (status == AnimationStatus.dismissed) {
print('Animation Dismissed');
_controller.forward();
}
});
// 开始动画
_valueController.forward();
...
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Animation'),
),
body: animation(context),
);
}
Widget animation(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
// 动态设置宽高
width: _doubleAnimation.value,
height: _doubleAnimation.value,
color: Colors.teal,
margin: EdgeInsets.all(10),
child: FlutterLogo(),
);
}
动画效果:

我们实现了缩放动画,我们也可以同样按照这个方式来实现旋转、渐变、位移、颜色变化等等复杂的动画。这里就不重复讲解了。
当然我们可以使用 Flutter 封装好的缩放动画组件:ScaleTransition。ScaleTransition 继承自 AnimatedWidget。
接下来我们看下 ScaleTransition 用法:
// 定义AnimationController
AnimationController _valueController =
AnimationController(duration: const Duration(seconds: 3), vsync: this);
Animation<double> _scaleAnimation = Tween(begin: 0.0, end: 2.0).animate(_valueController);
// 开始动画
_valueController.forward();
Widget scaleAnimation(BuildContext context) {
return ScaleTransition(
scale: _scaleAnimation,
child: Text('ScaleTransition'),
);
}
动画效果:

其他渐变、位移、旋转动画组件使用方法类似,这里就不重复讲解了。
3.Hero 动画的实现
在讲 Hero 动画前,先给大家来个铺垫,先看下页面跳转动画,也就是从一个页面跳转到另一个页面的页面跳转动画。其实在前面讲解路由的课程(第 2-5 课)里就给大家讲解了路由跳转的动画了:Route 在 Flutter 中主要有两种实现方法,一个是使用 MaterialPageRoute;另一个是使用 PageRouteBuilder 来构建。我们通过 MaterialPageRoute 和 PageRouteBuilder 也可以同时配置一个跳转动画。
如果使用 MaterialPageRoute 的话,那么 Flutter 默认的页面跳转动画是上下滑动切换。如果想像 iOS 那样左右滑动切换页面效果那就使用 CupertinoPageRoute 来替换 MaterialPageRoute 即可。
gotoPage() {
Navigator.push(context, MaterialPageRoute(builder: (context) {
return AnimationSample();
}));
}
...
void gotoPage() {
Navigator.push(context, CupertinoPageRoute(builder: (context) {
return AnimationSample();
}));
}
动画效果:

那如果这些页面跳转动画无法满足需求,那么我们就可以使用 PageRouteBuilder 来进行路由跳转,PageRouteBuilder 是支持配置跳转动画的。
我们再看下 PageRouteBuilder 的构造方法:
PageRouteBuilder({
// 路由设置
RouteSettings settings,
// 目标页面
@required this.pageBuilder,
// 跳转过度动画设置
this.transitionsBuilder = _defaultTransitionsBuilder,
this.transitionDuration = const Duration(milliseconds: 300),
this.opaque = true,
// 跳转过程中点击外部区域是否停止跳转
this.barrierDismissible = false,
this.barrierColor,
this.barrierLabel,
this.maintainState = true,
})
我们简单看一下具体的使用方法:
.push(context, PageRouteBuilder(
opaque: false,
// 跳转过渡背景色
barrierColor: Colors.blue,
// 跳转过程中点击外部区域是否停止跳转
barrierDismissible: false,
pageBuilder: (BuildContext context, Animation<double> animation,
Animation<double> secondaryAnimation) {
return ButtonSamples();
},
// 跳转过渡动画配置
transitionsBuilder: (BuildContext context, Animation<double> animation, Animation<double> secondaryAnimation, Widget child) {
return FadeTransition(
opacity: animation,
child: ScaleTransition(
scale: animation,
child: child,// 这里的child是pageBuilder里返回的目标页面
),
);
}
));
效果动画:
讲了个铺垫,那么我们进入正题:Hero 动画。
Hero 动画主要用于页面跳转切换时的某个 Widget 的过渡跳转动画效果,也叫共享元素过渡动画。用户从页面中选择一个元素(通常是一个图像),然后打开所选元素的详情页面。这个过程中元素和页面执行的动画就是 Hero 共享元素过渡动画。
例如我的一个页面有一个头像,点击头像跳到另一个页面,头像有一个动画,新页面打开也有一个过渡动画。
我们先看下 Hero 动画的基本使用方式:
- 先要在页面 A 和页面 B 分别定义一个 Hero Widget,并且设置相同的 tag 值,这样才可以匹配;
- 路由里配置从页面 A 跳转到页面 B;
- 点击跳转执行动画。
Hero 动画执行过程: Flutter 框架会根据这两个 Hero Widget 计算出一个补间矩形 ,将这个补间矩形作为一个中间的遮罩层作为动画过渡。在跳转过程中,页面 A 的 Hero Widget 会跳转到中间遮罩层,然后进入到页面 B。
整个的过程示意图如下:
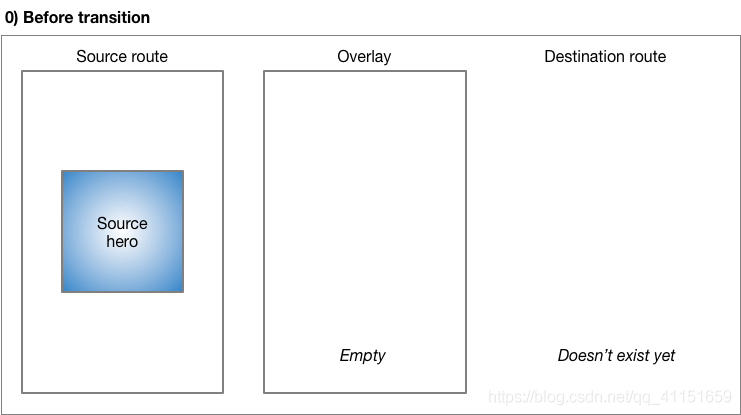
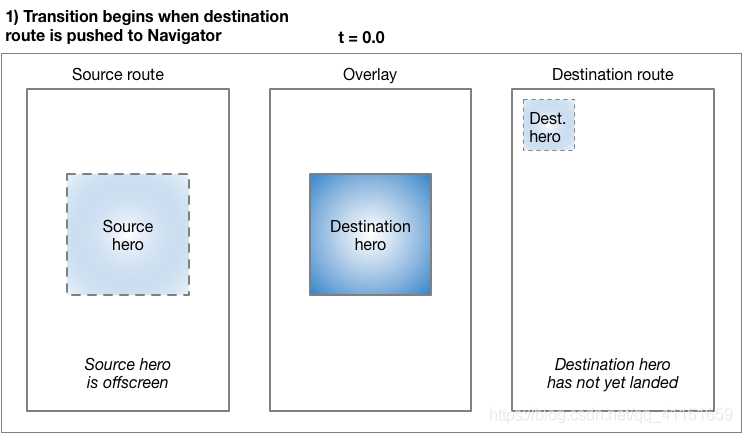
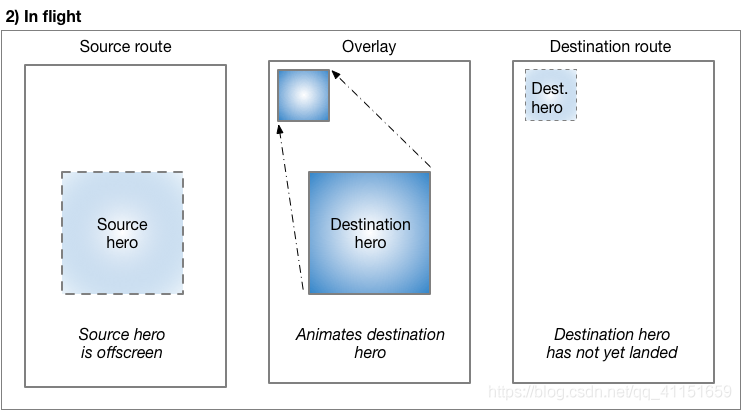
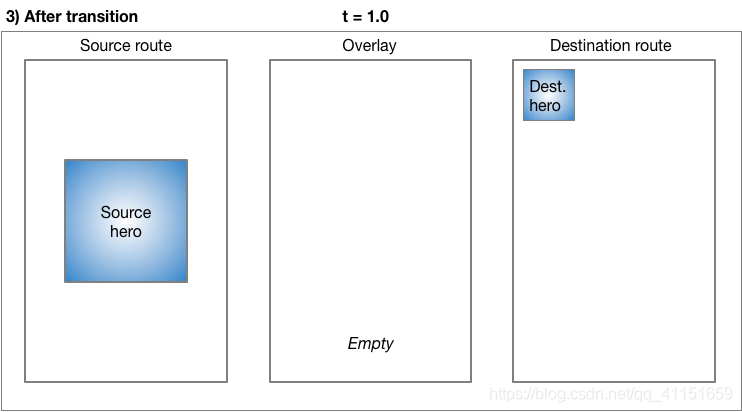
(以上图片来源于 Flutter 官方)
我们先看下 Hero 的构造方法:
const Hero({
Key key,
// tag标识标签
@required this.tag,
// 转变动画
this.createRectTween,
// 飞行过程中的Widget,可以自定义
this.flightShuttleBuilder,
// 构造占位Widget
this.placeholderBuilder,
// 手势滑动返回时是否有Hero动画
this.transitionOnUserGestures = false,
@required this.child,
})
我们在使用的时候非常的简单,Hero 包裹一个 Widget,如果设置点击事件的话用 InkWell 在 Hero 里再包裹一下这个 Wiget 即可。
我们看一个实例:
// 页面A定义一个Hero组件
// 用InkWell的话外面要包一个Material Widget
Hero(
// 相同tag
tag: "iconTag",
child: Material(
child: InkWell(
child: Icon(
Icons.room,
size: 70.0,
),
// 点击
onTap: () {
gotoPage();
},
),
));
...
// 点击后进行路由跳转
void gotoPage() {
Navigator.push(context, MaterialPageRoute(builder: (context) {
return HeroSamples();
}));
}
...
// 页面B,也要定义一个相同tag的Hero组件
class HeroSamplesState extends State<HeroSamples> {
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text('Hero'), primary: true),
body: Column(
children: <Widget>[
Hero(
// 相同tag
tag: "iconTag",
child: Icon(
Icons.room,
size: 70.0,
),
),
],
),
);
}
}
动画效果如下:
Hero动画效果

Hero 径向动画
我们再拓展一个官方的新的 Hero 径向动画,也就是从一个圆形的 Widget 经过动画变换成为矩形 Widget。
原理过程示意图如下:
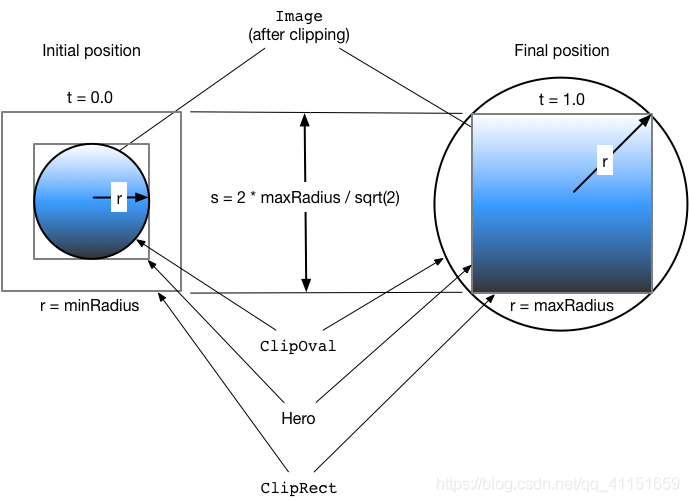
(图片来自 Flutter 官方)
我们看下简单用法:
Hero(
tag: "radialTag",
child: Material(
child: InkWell(
child: ClipOval(
child: SizedBox(
width: 100,
height: 100,
child: ClipRect(
child: Image.asset(
"assets/image_appbar.jpg",
fit: BoxFit.contain,
),
),
),
),
onTap: () {
gotoPage();
},
),
))
...
// 目标页
Hero(
tag: "radialTag",
child: Image.asset(
"assets/image_appbar.jpg",
fit: BoxFit.contain,
),
),
动画效果图:

4.交错动画的实现
Flutter 官方最新也推出了交错动画(StaggeredAnimation),也就是将很多个不同的动画效果叠加在一起来同时控制。也可以理解为一系列动画的组合,如:渐变、缩放、颜色、宽高等动画效果叠加在一起。
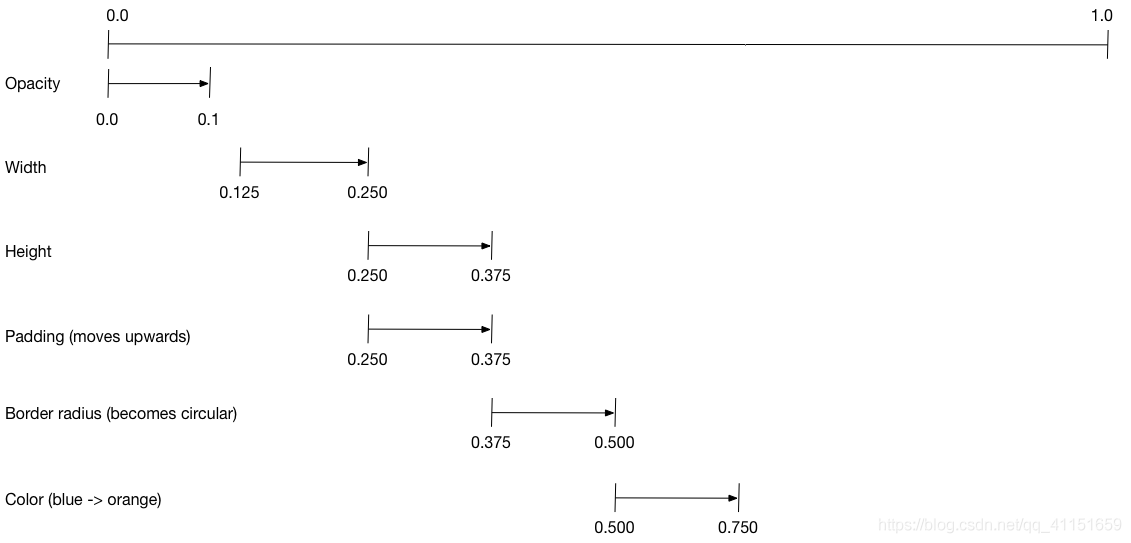
(图片来源于 Flutter 官方)
交错动画需要创建多个动画对象、一个 AnimationController 控制所有动画。
我们看一个官方实例:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class StaggerAnimationSamples extends StatefulWidget {
@override
State<StatefulWidget> createState() {
return StaggerAnimationSamplesState();
}
}
class StaggerAnimationSamplesState extends State<StaggerAnimationSamples>
with TickerProviderStateMixin {
AnimationController _controller;
Animation<double> opacity;
Animation<double> width;
Animation<EdgeInsets> padding;
Animation<BorderRadius> borderRadius;
Animation<Color> color;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_controller = AnimationController(
duration: const Duration(milliseconds: 5000), vsync: this);
opacity = Tween<double>(
begin: 0.0,
end: 1.0,
).animate(
CurvedAnimation(
parent: _controller,
curve: Curves.ease,
),
)..addListener(() {
setState(() {
// 动画值更新UI
});
});
width = Tween<double>(
begin: 50.0,
end: 150.0,
).animate(
CurvedAnimation(
parent: _controller,
curve: Curves.linear,
),
)..addListener(() {
setState(() {
// 动画值更新UI
});
});
borderRadius = BorderRadiusTween(
begin: BorderRadius.circular(4.0),
end: BorderRadius.circular(75.0),
).animate(
CurvedAnimation(
parent: _controller,
curve: Interval(
0.375,
0.500,
curve: Curves.ease,
),
),
)..addListener(() {
setState(() {
// 动画值更新UI
});
});
padding = Tween<EdgeInsets>(
begin: EdgeInsets.only(left: 0.0),
end: EdgeInsets.only(left: 80.0),
).animate(
CurvedAnimation(
parent: _controller,
curve: Interval(
0.5,
1.0,
curve: Curves.ease,
),
),
)..addListener(() {
setState(() {
// 动画值更新UI
});
});
color = ColorTween(
begin: Colors.blue,
end: Colors.teal,
).animate(
CurvedAnimation(
parent: _controller,
curve: Interval(
0.0,
0.8,
curve: Curves.ease,
),
),
)..addListener(() {
setState(() {
// 动画值更新UI
});
});
}
Future<Null> _playAnimation() async {
try {
await _controller.forward().orCancel;
await _controller.reverse().orCancel;
} on TickerCanceled {
// the animation got canceled, probably because we were disposed
}
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text('StaggerAnimation'), primary: true),
body: Column(
children: <Widget>[
RaisedButton(
child: Text("开始"),
onPressed: () {
_playAnimation();
},
),
Container(
width: 300.0,
height: 300.0,
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: Colors.black.withOpacity(0.1),
border: Border.all(
color: Colors.black.withOpacity(0.5),
),
),
child: Container(
padding: padding.value,
alignment: Alignment.bottomCenter,
child: Opacity(
opacity: opacity.value,
child: Container(
width: width.value,
height: width.value,
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: color.value,
border: Border.all(
color: Colors.indigo[300],
width: 3.0,
),
borderRadius: borderRadius.value,
),
),
),
),
),
],
),
);
}
}
动画效果如图:

那么关于 Flutter 的基本上全部动画都给大家讲解了,大家可以通过实践来巩固下。
5.总结
本节博客主要是给大家讲解了 Flutter 的动画的几种用法。
- 需要重点掌握的是基础动画、Hero 动画的用法。
- 实践一下这几种动画使用方法,并尝试组合几种动画实现一个复杂的交错动画。














