这一节我们就简单的介绍一下FactoryBean,知道这个接口的作用和意义,方便我们refresh()这个方法的理解
照旧,我们依旧先看源码,从源码中查看一下他的作用吧~

这次就不一句句翻译了(太多了),还是稍微大概的讲一下意思吧:FactoryBean是一个接口,任何一个Bean可以实现这个接口,那么这个bean将成为一个Factory,这个Factory将一些对象暴露出去,这些对象不一定是它们自己,返回的是一个Object对象,这个对象将通过getObject()暴露出去,并且支持单例和prototypes
这个接口有多重要?

看看这段:这个接口在spring自己的框架中被大篇幅的运用到,举例来说,AOP中link org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean和org.springframework.jndi.JndiObjectFactoryBean
但是他在非底层代码建设之外并不常见~
好了,看了官方的注释,还是有点模糊的吧,不过我们可以再看看ProxyFactoryBean这个官方的代码,其实看名字,“代理”,这个接口可以用于代理,想想也是,“任何bean实现了BeanFactory都可以通过getObject()这个方法去返回一个Object类型的bean,这个就很重要了”
接下来,还是老规矩,我们举个例子,来具体说明这个接口的作用,我们也做一个Proxy,通过切换注入数据库的名字,切换给出的数据库操作,如果我们注入MySQL我们就可以操作数据到mysql,如果注入Redis我们可以操作数据到redis
首先定义一个数据库操作接口
DBOperation.Java
1. <span style="color:#000000;">package org.study.spring.factorybean;
2.
3. /**
4. *
5. * 数据库操作对象
6. */
7. public interface DBOperation<T extends DBEntity> {
8.
9. int save(T t);
10.
11. int update(T t);
12.
13. int delete(T t);
14.
15. T select(Integer id);
16.
17.
18. }</span>
DBEntity.java
1. <span style="color:#000000;">package org.study.spring.factorybean;
2.
3. /**
4. *
5. * 数据库保存对象
6. *
7. */
8. public class DBEntity {
9.
10. private Integer id;
11.
12. public Integer getId() {
13. return id;
14. }
15.
16. public void setId(Integer id) {
17. this.id = id;
18. }
19.
20.
21. }</span>
MysqlDB.java
1. <span style="color:#000000;">package org.study.spring.factorybean;
2.
3. /**
4. * mysql数据操作
5. * @author
6. *
7. */
8. public class MysqlDB implements DBOperation<MysqlDBEntity>{
9.
10. public int save(MysqlDBEntity t) {
11. "save object to mysql");
12. return 1;
13. }
14.
15. public int update(MysqlDBEntity t) {
16. "update object to mysql");
17. return 0;
18. }
19.
20. public int delete(MysqlDBEntity t) {
21. "delete object from mysql");
22. return 0;
23. }
24.
25. public MysqlDBEntity select(Integer id) {
26. return new MysqlDBEntity();
27. }
28. }</span>
RedisDB.java
1. <span style="color:#000000;">package org.study.spring.factorybean;
2.
3.
4. /**
5. *
6. * redis数据库操作
7. *
8. */
9. public class RedisDB implements DBOperation<RedisDBEntity>{
10.
11. public int save(RedisDBEntity t) {
12. "save this object"+t.getJsonStr());
13. return 1;
14. }
15.
16. public int update(RedisDBEntity t) {
17. "update this object"+t.getJsonStr());
18. return 0;
19. }
20.
21. public int delete(RedisDBEntity t) {
22. "delete this object"+t.getJsonStr());
23. return 1;
24. }
25.
26. public RedisDBEntity select(Integer id) {
27. "select this object by id "+id);
28. return new RedisDBEntity();
29. }
30.
31.
32. }</span>
MysqlDBEntity.java
1. <span style="color:#000000;">package org.study.spring.factorybean;
2.
3.
4. public class MysqlDBEntity extends DBEntity{
5.
6. private String attribute;
7.
8. public String getAttribute() {
9. return attribute;
10. }
11.
12. public void setAttribute(String attribute) {
13. this.attribute = attribute;
14. }
15.
16. }</span>
RedisDBEntity.java
1. <span style="color:#000000;">package org.study.spring.factorybean;
2.
3. public class RedisDBEntity extends DBEntity {
4.
5. private String jsonStr;
6.
7. public String getJsonStr() {
8. return jsonStr;
9. }
10.
11. public void setJsonStr(String jsonStr) {
12. this.jsonStr = jsonStr;
13. }
14.
15.
16. }</span>
ProxyDBObject.java
1. <span style="color:#000000;">package org.study.spring.factorybean;
2.
3. import org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean;
4.
5.
6. /**
7. *
8. * DB代理,根据用户注入数据库的名称,自动返回对应的数据库操作给用户
9. *
10. */
11. public class ProxyDBObject implements FactoryBean<Object>{
12.
13. private String currentDB;
14.
15.
16. public String getCurrentDB() {
17. return currentDB;
18. }
19.
20. public void setCurrentDB(String currentDB) {
21. this.currentDB = currentDB;
22. }
23.
24. public Object getObject() throws Exception {
25. if("mysql".equals(currentDB)){
26. return new MysqlDB();
27. }
28. return new RedisDB();
29. }
30.
31. public Class<?> getObjectType() {
32. if("mysql".equals(currentDB)){
33. return MysqlDB.class;
34. }
35. return RedisDB.class;
36. }
37.
38. public boolean isSingleton() {
39. return false;
40. }
41.
42.
43.
44.
45. }</span>
factory-bean.xml
1. <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2. <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
3. xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
4. xmlns:mybatis-spring="http://mybatis.org/schema/mybatis-spring"
5. xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee"
6. xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
7. http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd
8. http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee-3.2.xsd
9. http://mybatis.org/schema/mybatis-spring http://mybatis.org/schema/mybatis-spring-1.2.xsd
10. >
11.
12.
13.
14. <bean id="proxyDB" class="org.study.spring.factorybean.ProxyDBObject">
15. <property name="currentDB" value="mysql"/>
16. </bean>
17.
18. </beans>ProxyDBObjectTest.java
当配置currentDB为“mysql”时,运行结果是:
1. package org.study.spring.factorybean;
2.
3. import org.junit.Test;
4. import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
5. import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
6.
7. public class ProxyDBObjectTest{
8.
9.
10. @Test
11. public void test2() throws Exception{
12. new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("factory-bean.xml");
13. "proxyDB",DBOperation.class);
14. new MysqlDBEntity();
15. dBoperation.save(dbEntity);
16. }
17.
18. }
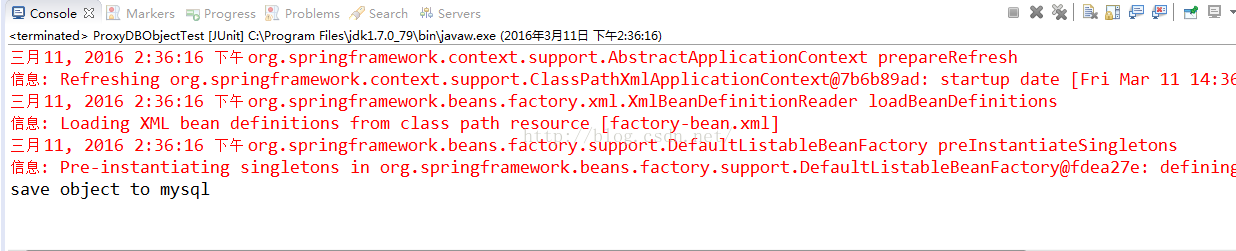
切换到redis会报错,因为我们保存的对象是mysqlDBEntity,转换异常
真实开发环境中,可以有2个开发人员,一个写mysql的保存,一个写redis的保存~
举了这么一个例子,其实就只是帮助大家稍微理解一下factoryBean干嘛的,相当于beanfactory.getbean这个返回的bean就是factorybean中getObject中返回的对象
那我们怎么才能够通过beanfactory获取factorybean呢,嘿嘿,其实beanfactory源码中已经有了说明:
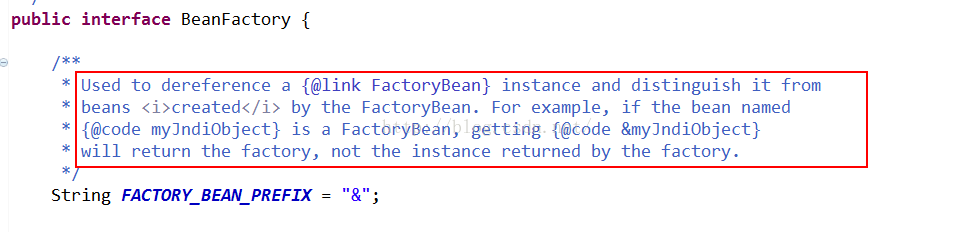
通过前缀引用来区分本身和factoryBean,举例说明,如果一个bean叫做myJndiObject,那么getBean("myJndiObject")将获取该bean,如果getBean("&myJndiObject")将获取FactoryBean
修改上面的ProxyDBObjectTest.java
1. <span style="color:#000000;">package org.study.spring.factorybean;
2.
3. import org.junit.Test;
4. import org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean;
5. import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
6. import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
7.
8. public class ProxyDBObjectTest{
9.
10.
11. @Test
12. public void test2() throws Exception{
13. new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("factory-bean.xml");
14. "&proxyDB",FactoryBean.class);
15. DBOperation db = (DBOperation)factoryBean.getObject();
16. new MysqlDBEntity();
17. db.save(dbEntity);
18. }
19.
20. }</span>
"&"符号可以获取本身,其实吧,BeanFactory和FactoryBean根本没有本质的关联,而且他们都是根接口,没有紧密的关系
关于FactoryBean在Aop中的运用,我们到了AOP再说,我们还是先分析IoC吧~
