Step 1:Bundle构建、加载、更新
(1)搭建Build工具
AB包的意义:如果我们将资源都放在Resources中,我们客户端的大小会越来越大。所以我们希望将资源打包放到服务端,使用的时候客户端到服务端去下载,这样就可以达到缩包的效果。
1)导入xLua
将xlua中Asset目录下的文件保持这个结构拖到我们的项目中。
2)查找BuildResources下的资源文件
进行格式转换和拼接
查找依赖资源
3)使用BuildPipeline构建AB包
BundleBuild策略:
|
按文件夹打包 |
按文件打包 |
优势 |
Bundle的数量少 |
更新的补丁小 |
劣势 |
后期更新的时候补丁大 |
首次下载的时候慢 |
打包的代码参考:
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using UnityEditor;
using UnityEngine;
public class BuildTool : Editor
{
[MenuItem("Tools/Build Windows Bundle")]
static void BundleWindowsBuild()
{
Build(BuildTarget.StandaloneWindows);
}
[MenuItem("Tools/Build Android Bundle")]
static void BundleAndroidBuild()
{
Build(BuildTarget.Android);
}
[MenuItem("Tools/Build IOS Bundle")]
static void BundleIOSBuild()
{
Build(BuildTarget.iOS);
}
static void Build(BuildTarget target)
{
List<AssetBundleBuild> assetBundleBuilds = new List<AssetBundleBuild>();
List<string> bundleInfos = new List<string>();
string[] files = Directory.GetFiles(PathUtil.BuildResourcesPath, "*", SearchOption.AllDirectories);
for (int i=0; i<files.Length; i++)
{
if (files[i].EndsWith(".meta")) continue;//meta文件是不用打包的
AssetBundleBuild assetBundle = new AssetBundleBuild();
string fileName = PathUtil.GetStandardPath(files[i]);//文件的格式进行标准化
Debug.Log("FileName : " + fileName);
string assetName = PathUtil.GetUnityPath(fileName);//截取asset之后的部分作为assetname属性
assetBundle.assetNames = new string[] { assetName };
Debug.Log("AssetName: " + assetName );
string bundleName = fileName.Replace(PathUtil.BuildResourcesPath, "").ToLower();//标准化之后将BuildResource以及之前的部分都替换掉,作为Bundle的名字
assetBundle.assetBundleName = bundleName + ".ab";//Bundle的后缀改为ab
Debug.Log("AssetBundleName: " + bundleName + ".ab");
assetBundleBuilds.Add(assetBundle);
//添加依赖信息
List<string> dependenceInfo = GetDependence(assetName);
string bundleInfo = assetName + "|" + bundleName + ".ab";
if (dependenceInfo.Count > 0)
bundleInfo = bundleInfo + "|" + string.Join("|", dependenceInfo);
bundleInfos.Add(bundleInfo);
}
if (Directory.Exists(PathUtil.BundleOutPath)) Directory.Delete(PathUtil.BundleOutPath, true);
//创建输出的目标
Directory.CreateDirectory(PathUtil.BundleOutPath);
//这个就是打包
BuildPipeline.BuildAssetBundles(PathUtil.BundleOutPath, assetBundleBuilds.ToArray(), BuildAssetBundleOptions.None, target);
File.WriteAllLines(PathUtil.BundleOutPath + "/" , bundleInfos);
AssetDatabase.Refresh();
}
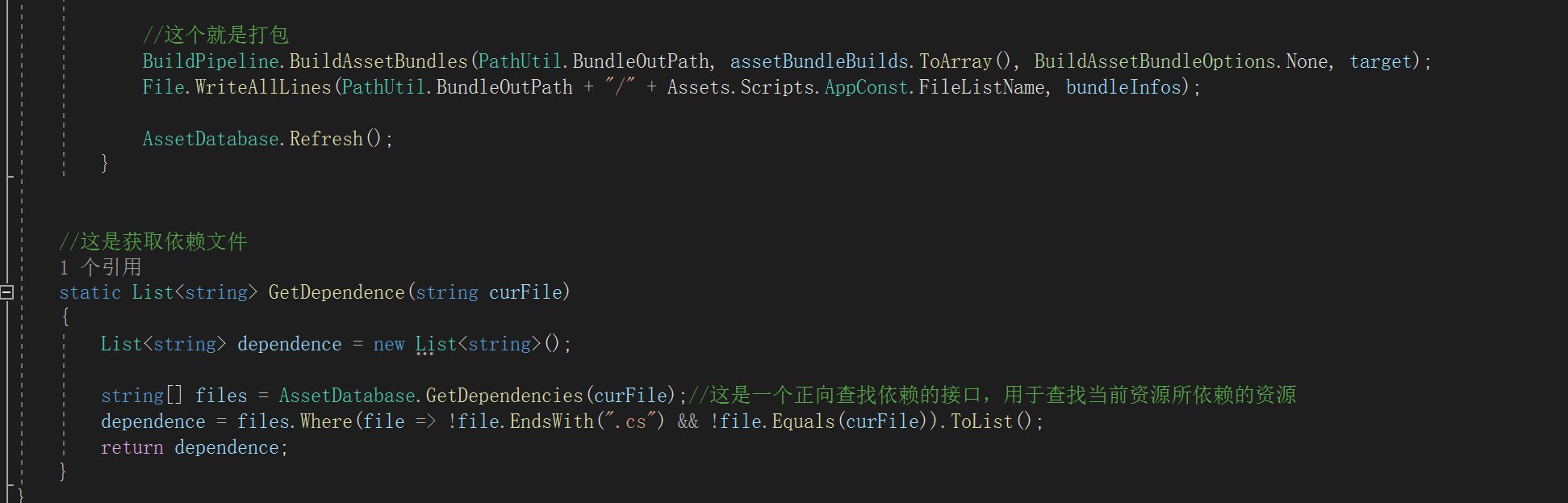
//这是获取依赖文件
static List<string> GetDependence(string curFile)
{
List<string> dependence = new List<string>();
string[] files = AssetDatabase.GetDependencies(curFile);//这是一个正向查找依赖的接口,用于查找当前资源所依赖的资源
dependence = files.Where(file => !file.EndsWith(".cs") && !file.Equals(curFile)).ToList();
return dependence;
}
}
点击运行之后创建的文件:
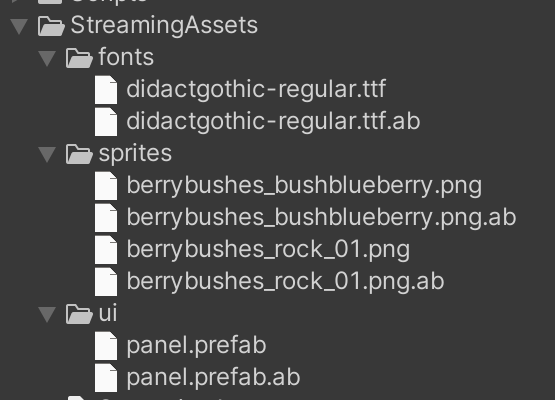
4)加载AB资源:
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class LoadAB : MonoBehaviour
{
IEnumerator Start()
{
AssetBundleCreateRequest request = AssetBundle.LoadFromFileAsync(Application.streamingAssetsPath + "/ui/panel.prefab.ab");
yield return request;
AssetBundleRequest bundleRequest = request.assetBundle.LoadAssetAsync("Assets/BuildResources/UI/Panel.prefab");
yield return bundleRequest;
GameObject go = Instantiate(bundleRequest.asset) as GameObject;
go.transform.SetParent(this.transform);
go.SetActive(true);
go.transform.localPosition = Vector3.zero;
}
}
但是这种方式如果依赖资源没有加载,会造成依赖资源的丢失。
(2)建立版本管理系统
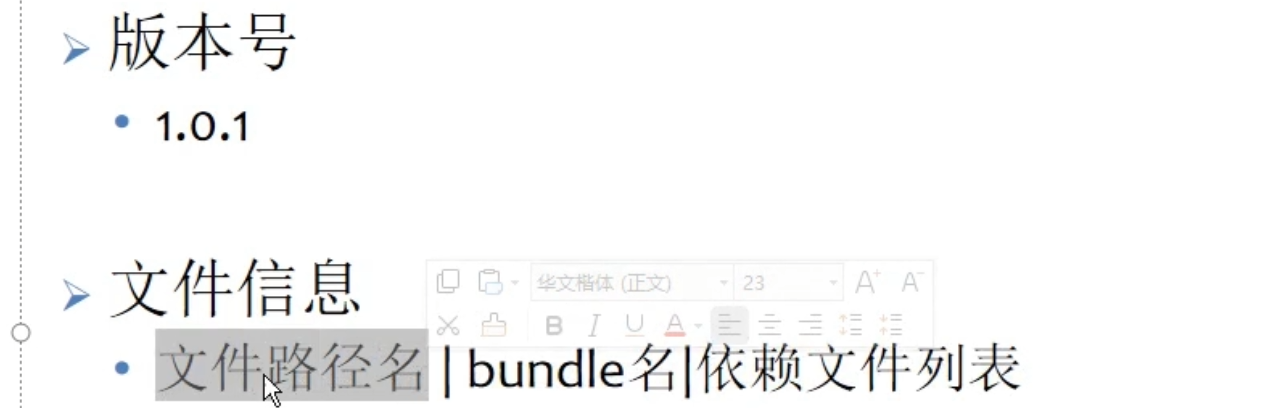
版本信息管理:
查找依赖文件并且进行保存:
(3)资源管理器
接着我们创建一个资源管理器进行文件的加载。
using Assets.Scripts;
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using UnityEngine;
using UObject = UnityEngine.Object;
public class ResourceManager : MonoBehaviour
{
internal class BundleInfo
{
public string AssetName;
public string BundleName;
public List<string> Dependences;
}
//存放bundle信息
private Dictionary<string, BundleInfo> m_BundleInfos = new Dictionary<string, BundleInfo>();
public void ParseVersionFile()
{
//拿到版本文件路径
string url = Path.Combine(PathUtil.BundleResourcePath, AppConst.FileListName);//框架层
//读取
string[] data = File.ReadAllLines(url);//一行一行的读
//解析文件信息
for (int i = 0; i < data.Length; i++)
{
BundleInfo bundleInfo = new BundleInfo();
string[] info = data[i].Split('|');//分割
bundleInfo.AssetName = info[0];//这个是filelist里面的名字
bundleInfo.BundleName = info[1];//这个是打好Bundle包之后的资产地址
//数组,可以动态扩容
bundleInfo.Dependences = new List<string>(info.Length - 2);
for (int j = 2; j < info.Length; j++)//索引从2开始才是依赖资源
{
bundleInfo.Dependences.Add(info[j]);
}
m_BundleInfos.Add(bundleInfo.AssetName, bundleInfo);
//if (info[0].IndexOf("LuaScripts") > 0)
// Manager.Lua.LuaNames.Add(info[0]);
}
}
//internal void LoadLua(string name, Action<UObject> p)
//{
// throw new NotImplementedException();
//}
//异步加载资源
IEnumerator LoadBundleAsync(string assetName, Action<UObject> action = null)
{
//获取文件信息
string bundleName = m_BundleInfos[assetName].BundleName;
string bundlePath = Path.Combine(PathUtil.BundleResourcePath, bundleName);
List<string> dependences = m_BundleInfos[assetName].Dependences;
if (dependences != null && dependences.Count > 0)
{
//递归加载依赖资源
for (int i = 0; i < dependences.Count; i++)
{
yield return LoadBundleAsync(dependences[i]);
}
}
//加载Bundle资源
AssetBundleCreateRequest request = AssetBundle.LoadFromFileAsync(bundlePath);
yield return request;
AssetBundleRequest bundleRequest = request.assetBundle.LoadAssetAsync(assetName);
yield return bundleRequest;
Debug.Log("This is LoadBundleAsync");
action?.Invoke(bundleRequest?.asset);
}
#if UNITY_EDITOR
void EditorLoadAsset(string assetName, Action<UObject> action = null)
{
Debug.Log("This is EditorMode");
UObject obj = UnityEditor.AssetDatabase.LoadAssetAtPath(assetName, typeof(UObject));
if (obj == null)
Debug.LogError("Assets name does not exists: " + assetName);
action?.Invoke(obj);
}
#endif
public void LoadAsset(string assetName, Action<UObject> action)
{
#if UNITY_EDITOR
if (AppConst.gameMode == GameMode.EditorMode)
EditorLoadAsset(assetName, action);
else
#endif
StartCoroutine(LoadBundleAsync(assetName, action));
}
public void LoadUI(string assetName, Action<UObject> action = null)
{
LoadAsset(PathUtil.GetUIPath(assetName), action);
}
public void LoadMusic(string assetName, Action<UObject> action = null)
{
LoadAsset(PathUtil.GetMusicPath(assetName), action);
}
public void LoadSound(string assetName, Action<UObject> action = null)
{
LoadAsset(PathUtil.GetSoundPath(assetName), action);
}
public void LoadEffect(string assetName, Action<UObject> action = null)
{
LoadAsset(PathUtil.GetEffectPath(assetName), action);
}
public void LoadScene(string assetName, Action<UObject> action = null)
{
LoadAsset(PathUtil.GetScenePath(assetName), action);
}
public void LoadLua(string assetName, Action<UnityEngine.Object> action = null)
{
LoadAsset(assetName, action);
}
public void LoadPrefab(string assetName, Action<UnityEngine.Object> action = null)
{
LoadAsset(assetName, action);
}
}
(4)热更新部分
热更新的方案选择:
|
整包 |
分包 |
含义 |
完整资源放在包内 |
|
优势 |
首次更新时间少 |
安装包下载快 |
劣势 |
安装包下载时间长,首次安装事件久 |
首次更新时间久 |
热更新的步骤:
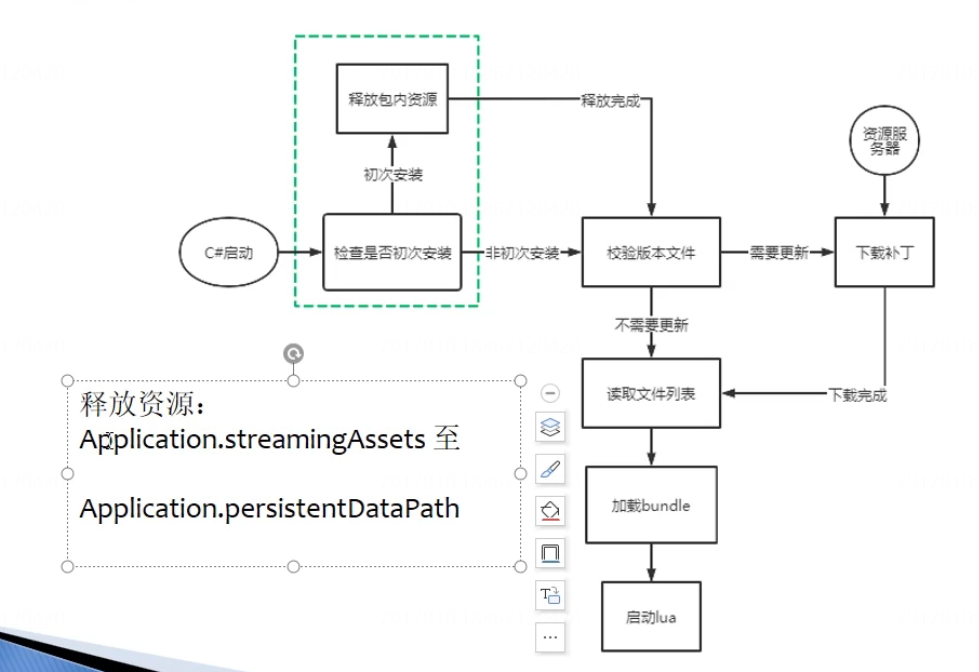
整包策略:streamingasset是只读的,persistentDataPath是可读写的。初次安装的时候将只读目录的内容拷贝到可读写目录,后续检查更新也都是从可读写目录进行更新下载的。
分包策略:直接和可读写目录进行交互。
热更新代码部分:
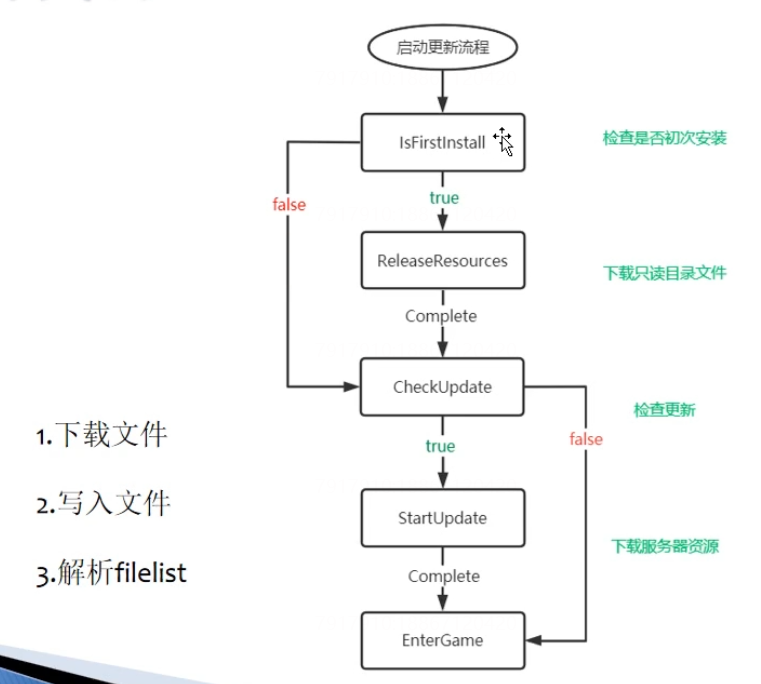
检测初次安装:只读目录有热更新资源、可读写目录没有热更资源、判断filelist文件是否存在。需要注意filelist需要最后写入
检查更新:下载资源服务器上的filelist,对比文件信息和本地是否一致
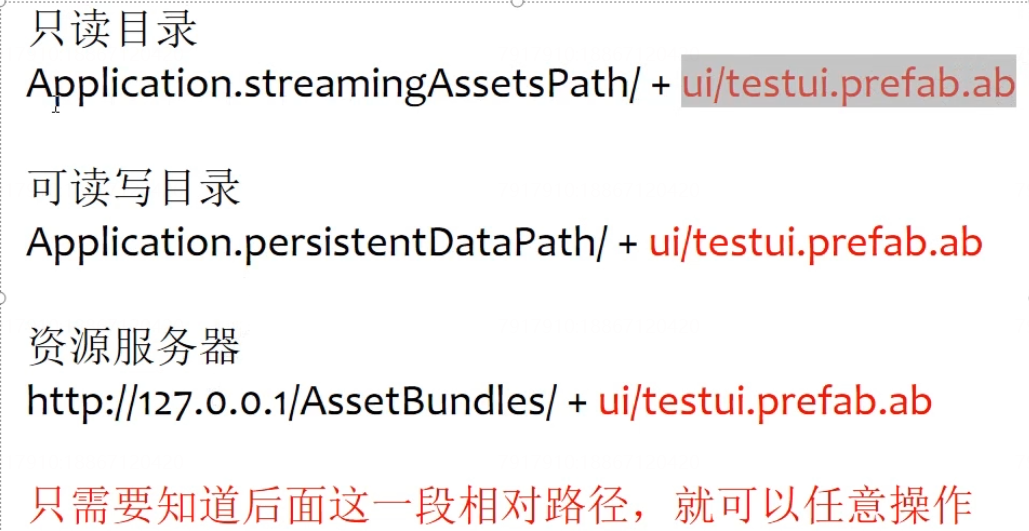
热更新代码步骤
1)下载文件并完成文件释放
需要提前在创建只读目录和可读写目录
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.Networking;
public class HotUpdate : MonoBehaviour
{
internal class DownFileInfo
{
public string url;
public string fileName;
public DownloadHandler fileData;
}
//下载文件
IEnumerator DownLoadFile(DownFileInfo info,Action<DownloadHandler> Complete)
{
UnityWebRequest webRequest = UnityWebRequest.Get(info.url);
yield return webRequest.SendWebRequest();
//检测
if(webRequest.isHttpError || webRequest.isNetworkError)
{
Debug.Log("下载文件出错"+ info.url);
yield break;
}
info.fileData = webRequest.downloadHandler;
Complete?.Invoke(info);
//下载完成之后需要释放掉
webRequest.Dispose();
}
//下载多个文件
IEnumerator DownLoadFile(List<DownFileInfo> infos, Action<DownloadHandler> Complete, Action DownLoadAllComplete)
{
foreach(DownFileInfo info in infos)
{
yield return DownLoadFile(info, Complete);
}
DownLoadAllComplete?.Invoke();
}
}
Step 2: 热更新管理器
(1)Lua加载和管理
(2)Lua绑定和执行
Step 3:业务逻辑管理器






